Food infection and food intoxication pdf
Food infection and food intoxication pdf
This edition of Foodborne Infections and Intoxications updates the third edition, published in 2006, with increased emphasis on global disease prevention and a risk-based approach to food safety. This text is particularly valuable for students and practitioners in the fields of public health and food safety. It can also serve as a useful reference for public health investigators and officials.
Food Poisoning and Food Infection – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Food poisoning is a food borne disease. Ingestion of food that contains a toxin, chemical or infectious agent (like a bacterium, virus, parasite, or prion) may cause adverse symptoms in the body.
Article (PDF Available) conducted to assess sanitary conditions and food handling practice of restaurants in Jimma town for the implication of food born infection and food intoxication. Out of
Scientific Committee on Enteric Infections and Foodborne Diseases Review of Staphylococcal Food Poisoning in Hong Kong Purpose This paper reviews the latest global and local epidemiology of staphylococcal food poisoning and examines the public health measures for prevention and control the disease. Bacteriology 2. Staphylococcus aureus is a non-motile facultative anaerobic Gram-positive …
Food Poisoning Food Poisoning 2010 5 Intoxications Intoxication involves food poisoning in which the organism grows in food and releases a toxin from the cells.
Sponsored by the Marler Clark hepatitis A lawyers. Hepatitis A (HAV) is a virus that can be foodborne or passed from person to person. Hepatitis A infection…
poisoning, the microbes multiply readily in the food prior to consumption, whereas in food-borne infection, food is merely the vector for microbes that do not grow on their transient substrate. Others consider food poisoning as
Clostridium perfringens is a fairly common form of food poisoning that is commonly confused with the 24-hr flu. It is often called the “food service germ,” since it often comes from food in large quantities left out at a dangerous temperature. Symptoms generally include abdominal pain and stomach…
Food poisoning caused by the bacteria Listeria can cause problems for unborn babies, and E. coli infection can cause problems with the kidneys. Other complications can include arthritis and bleeding problems. Non-infectious food poisoning can occasionally lead …
7. Most foodborne illnesses demonstrate seasonal changes. Food poisoning outbreaks are more common in summer (June to September) and winter (December to February) months (Figure 4).
food borne infections and intoxications Download food borne infections and intoxications or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format.
Intoxication: The term “food poisoning” generally refers to foodborne intoxication and illness brought about by the toxins present in food or water which are produced by certain bacteria on or in them, as well as the unhygienic handling and preparation of food. Foodborne intoxication may also be caused by toxins produced to the presence of heavy metals, chemicals and foreign substances in
Food contamination occurring with staphylococcal food poisoning: -foods with starch or cream base are more likely to be contaminated -cream pies, dairy products, poultry products, meat and meat products and picnic foods such as potato salad are common problem areas
Food Safety Awareness 1. What is Bacillus cereus food intoxication?food intoxication? Well recognized as a cause of “food poisoning” or “foodborne disease”, Bacillus cereus (bah-CILL-
B. cereus food poisoning can be caused by either ingesting large numbers of bacterial cells and/or spores in contaminated food (diarrhoeal type) or by ingesting food …
Staphylococcal food intoxication is an intoxication (not an infection) of abrupt and sometimes violent onset, with severe nausea, cramps, vomiting and prostration. It is often accompanied by diarrhea and sometimes subnormal temperature and lowered blood pressure. Deaths are rare. Duration of illness is commonly not more than one to two days, but the intensity of symptoms may require
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning

Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
5/07/2010 · 1. Staphylococcal Food Poisoning. Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP) is an intoxication that results from the consumption of foods containing sufficient amounts of one (or more) preformed enterotoxin [1,2].
food poisoning and foor infections Download food poisoning and foor infections or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get food poisoning and foor infections book now.
This is the most common type of food-poisoning caused due to the food contaminated with a potent toxin, namely, enterotoxin. This toxin is produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. A sudden onset of illness starts usually within 3 to 6 hours after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Title: Graphic organizer – Food Safety: Infection vs. Intoxication (Key) Author: Baylor University, Statewide Instructional Resources Development Center
Shigella is a bacterium that can cause sudden and severe diarrhea (gastroenteritis) in humans. Shigellosis, the disease caused by infection with Shigella, is characterized by symptoms such as painful abdominal cramping, vomiting, and diarrhea.
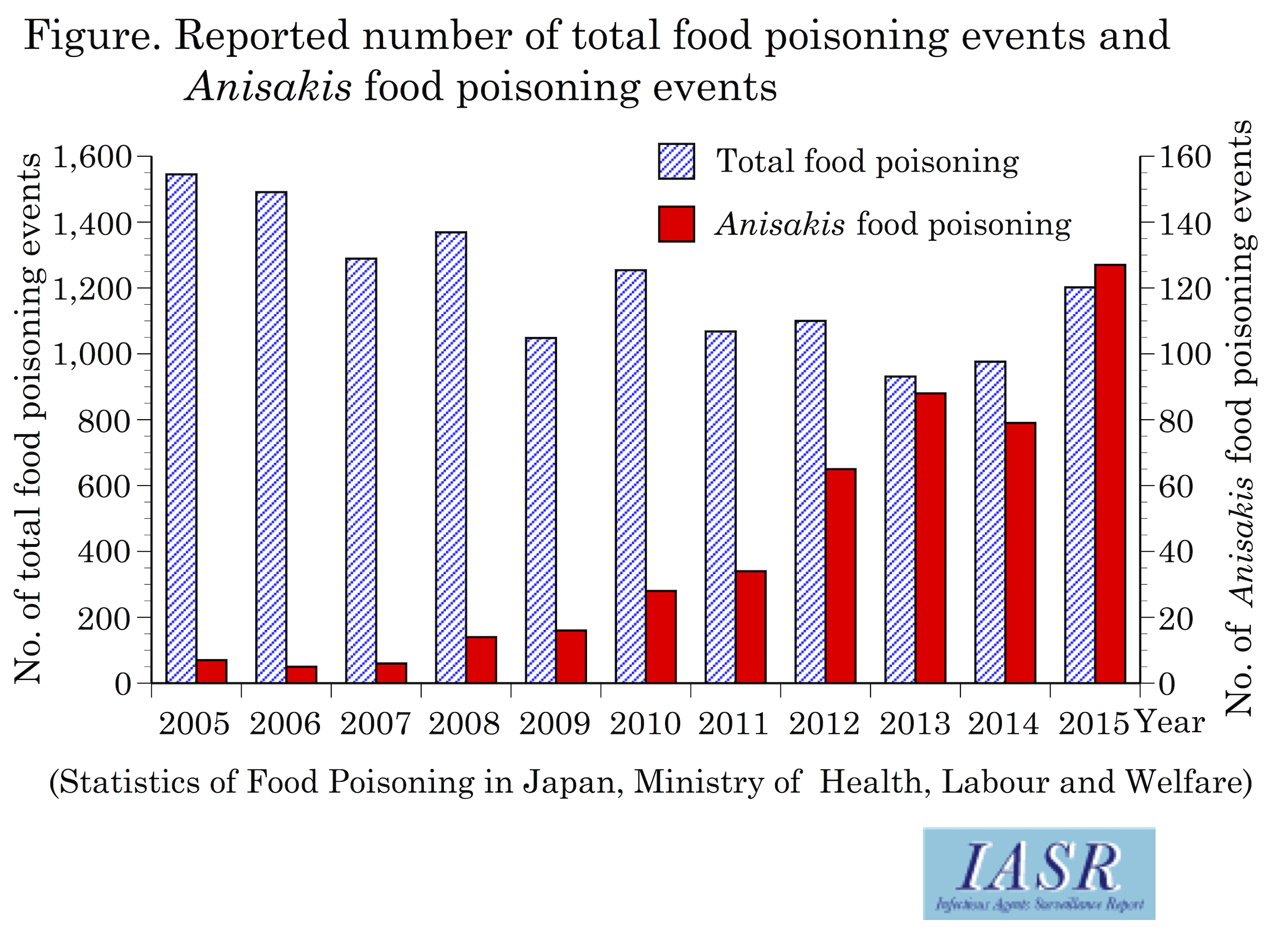
food poisoning food borne infection and intoxication Download food poisoning food borne infection and intoxication or read online here in PDF or EPUB.
These microorganisms can cause one of three types of illness — infection, intoxication, or toxin-mediated infection. Infection A foodborne disease is when a person eats food containing harmful microorganisms, which then grow in the intestinal tract and cause illness.
If you have food poisoning, chances are it won’t go undetected. Symptoms can vary depending on the source of the infection. The length of time it takes for symptoms to appear also depends on the
Food poisoning, also called foodborne illness, is illness caused by eating contaminated food. Infectious organisms — including bacteria, viruses and parasites — or their toxins are the most common causes of food …
Foodborne bacterial intoxication is caused by the ingestion of food containing preformed bacterial toxin, such as the toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium botulinum, resulting from bacterial growth in the food. Foodborne infection, on the other hand, is caused by ingestion of food containing viable bacteria such as Salmonella or Listeria which then grow and establish
Food poisoning can occur if food or water is contaminated with the stools (faeces) of infected cats. It can also occur if raw or undercooked meat from another animal carrying the parasite is eaten. The infection is known as toxoplasmosis. Symptoms of this type of food poisoning include swollen lymph glands and sometimes a skin rash.
A wide variety of foods and food products derived from plants and animals support the growth of pathogenic and toxigenic bacteria, resulting in food-borne diseases such as food infection and food
The University of Georgia College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension Service Preventing Food Poisoning And Food Infection
Food-borne botulism is a severe type of food poisoning caused by the ingestion of foods containing the potent neurotoxin formed during growth of the organism. The toxin is heat labile and can be destroyed if heated at 80°C for 10 min or longer. The incidence of the disease is low, but the disease is of considerable concern because of its high mortality rate if not treated immediately and
Download the PDF to view the article, as well as its associated figures and tables. Abstract Perhaps few other subjects in the field of scientific medicine have received so much revision and study in the past quarter century as has the subject of food infections and food intoxication.
“The text is an important source of information, necessary for reducing and eliminating infections and food-borne intoxications.”– Industrie Alimentari (Food …
What are the main differences between food borne infection
Food Intoxication Versus Food Infection Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing. United States Department of Agriculture. 7 . Signiicant Microorganisms in Food Production . Microorganisms such as molds, yeasts, and bacteria can grow in food and cause spoilage. Bacteria also can cause foodborne illness. Viruses and parasites, such as tapeworms, roundworms, and …
Diarrheal disease – food infection mediated by the production of enterotoxin within the small intestine (first recognized in an hospital outbreak caused by contaminated vanilla sauce in Oslo Norway.) Emetic disease – food intoxication caused by toxin released into food.
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home > allowing food to be at a temperature for more than four hours that allows bacteria to grow well. Keep food cold enough (fridge or freezer) or hot enough (steaming hot) to guard against bacterial growth. However, the bacteria Listeria will grow in refrigerators. Listeria is an important cause of illness in the elderly, immunocompromised persons and pregnant
The most common food-borne infections in the Czech Republic are salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis. The number of reported salmonellosis cases has declined in recent years, while
Listeria infection can be dangerous for pregnant women, the elderly and people whose immune systems are not working properly. Prevention is best – people at risk of listeria infection should avoid high risk foods. Listeria is an illness caused by eating foods contaminated by the bacteria, Listeria
A food borne intoxication is a disease that results from eating food contaminated with poisons or toxins from bacteria, molds, or chemicals. These toxins are usually odorless, tasteless and colorless,
Food poisoning and food infection are different, although the symptoms are similar. True food poisoning or food intoxication is caused by eating food that contains a toxin or poison due to bacterial growth in food.
Ad hoc Group on Foodborne Viral Infections. An update on viruses in the food chain . Page 2 of 136. Terms of reference . The Ad Hoc Group on Foodborne Viral Infections terms of reference are to – Assess the extent of viral foodborne infection in the UK – with particular reference to norovirus and hepatitis E. Including discussion on the issues surrounding emerging risks. Describe the – eating healthy on a budget pdf The term food poisoning is actually a catch-all term and is usually considered to be synonymous with “food-borne illness.” The term is broken down into food infection and food intoxication and with either one, you will have similar symptoms.
Both terms, foodborne illness and food poisoning, are often used interchangeably by consumers. However, both have different meanings. Foodborne illness is an infection or intoxication that results from eating food contaminated with viable (live) microorganisms or their toxins.
Staphylococcal food poisoning is a common disease whose real incidence is probably underestimated for a number of reasons, which include misdiagnosis, …
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and Intoxications J. Glenn Morris, Jr., and Morris E. Potter, editors ISBN: 978-0-12-416041-5 Academic Press, London, UK, 2013 Pages: 541; Price: US 9.95 The global supply of food has led to an increasingly connected planet, not only in terms of food products but also in terms of risks for foodborne diseases. The fourth edition of Mor-ris
Bacterial foodborne infections occur when food, that is contaminated with bacteria, is eaten and the bacteria continues to grow in the intestines, setting up an infection which causes illness. Salmonella, Campylobacter, hemorrhagic E. coli and Listeria all cause infections. Food intoxication results from consumption of toxins (or poisons) produced in food by bacterial growth. Toxins, not
An outbreAk of stAphylococcAl food poisoning in A commerciAlly cAtered buffet Alexis Pillsbury, May Chiew, John Bates, Vicky Sheppeard Abstract Staphylococcal food poisoning is a common cause . of foodborne illness. In Australia, since 2000, approximately 30% of foodborne. Staphylococcus aureus. outbreaks reported to OzFoodNet have been associated with foods prepared by com-mercial caterers
Muir and Ritchie (1921) were the first to describe the pathogenic properties of Bacterium coli associated with infections of the intestine and urinary tract, some cases of summer diarrhoea (cholera nostras), infantile diarrhoea and food poisoning.
It’s possible to get a staph infection from food poisoning, but a number of things have to happen first. This type of infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, or “staph
The various “intoxications” are different in how they make the patient feel, the onset time, the symptoms, and the final outcome. Similarly with food-borne infections – more than 250 different types (not including the 2000+ serotypes of Salmonella).
Diseases which result from pathogenic microorganisms are of two types: infection and intoxication. Foodborne infection is caused by the ingestion of food containing live bacteria which grow and establish themselves in the human intestinal tract.
Food borne diseases can be divided into food infection and food poisoning. The popular media tends to describe all food-related illnesses as “food poisoning”, but strictly speaking, this is incorrect.
00:01 In our discussion of Gastrointestinal Tract Infections, we come to the very large topic of Infectious Diarrhea and Food Poisoning. 00:13 We would certainly define it as the acute onset of excessive bowel movements caused either directly or indirectly by microbial pathogens.
food poisoning and food infections Download food poisoning and food infections or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get food poisoning and food infections book now.
Intoxication vs. infection Food-related illnesses fall generally into two categories: intoxication and infection. The term “food poisoning” applies most readily to the type of illnesses caused by toxins that may be in the food we eat.
Staphylococcal Food Intoxication Manitoba
SECTION 4_ADDITIONAL INFORMATION / 34 Information on Common Food Poisoning Bacteria INFO ON COMMON FOOD POISONING BACTERIA Bacteria are one of the most common causes of food poisoning.
Contamination of food items by pathogenic microorganisms is the cause for both food poisoning and food intoxication. However, the intoxication is only a way of occurrence of food poisoning. There are several other ways and means are available in the case of pathogenesis. A combination of intoxication, infection and toxicoinfection, collectively, can be recognized as food poisoning/ food borne
Food poisoning is illness resulting from consumption of contaminated food or water. Food can be contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, or by toxins produced by them. Food poisoning is one of the most common illnesses in Australia, with an estimated 4 to 7 million cases of foodborne illness each year.
Foodborne illnesses Diarrhoeal diseases are linked to the deaths of an estimated 2 million people annually – mostly children – and most of these illnesses, including foodborne illness, are attributed to contaminated food or water.
What’s the difference between food infection and food

Food Safety Education For Educators Competencies
Difference Between Food Poisoning and Food Intoxication

Food Poisoning (Food-borne Illness)
BACTERIAL FOOD INTOXICATION Request PDF


NC DPH Food Poisoning & Food-Borne Illnesses
Bacteria Associated with Foodborne Diseases IFT.org
– Food Infections and Food Intoxications. The JAMA Network
What is the difference between food infection and food


Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins
Causes and types of food poisoning MyMed.com
Foodborne Infections vs. Foodborne Intoxications
The various “intoxications” are different in how they make the patient feel, the onset time, the symptoms, and the final outcome. Similarly with food-borne infections – more than 250 different types (not including the 2000 serotypes of Salmonella).
Download the PDF to view the article, as well as its associated figures and tables. Abstract Perhaps few other subjects in the field of scientific medicine have received so much revision and study in the past quarter century as has the subject of food infections and food intoxication.
Food Intoxication Versus Food Infection Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing. United States Department of Agriculture. 7 . Signiicant Microorganisms in Food Production . Microorganisms such as molds, yeasts, and bacteria can grow in food and cause spoilage. Bacteria also can cause foodborne illness. Viruses and parasites, such as tapeworms, roundworms, and …
7. Most foodborne illnesses demonstrate seasonal changes. Food poisoning outbreaks are more common in summer (June to September) and winter (December to February) months (Figure 4).
This edition of Foodborne Infections and Intoxications updates the third edition, published in 2006, with increased emphasis on global disease prevention and a risk-based approach to food safety. This text is particularly valuable for students and practitioners in the fields of public health and food safety. It can also serve as a useful reference for public health investigators and officials.
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home > allowing food to be at a temperature for more than four hours that allows bacteria to grow well. Keep food cold enough (fridge or freezer) or hot enough (steaming hot) to guard against bacterial growth. However, the bacteria Listeria will grow in refrigerators. Listeria is an important cause of illness in the elderly, immunocompromised persons and pregnant
Food poisoning is a food borne disease. Ingestion of food that contains a toxin, chemical or infectious agent (like a bacterium, virus, parasite, or prion) may cause adverse symptoms in the body.
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and Intoxications J. Glenn Morris, Jr., and Morris E. Potter, editors ISBN: 978-0-12-416041-5 Academic Press, London, UK, 2013 Pages: 541; Price: US 9.95 The global supply of food has led to an increasingly connected planet, not only in terms of food products but also in terms of risks for foodborne diseases. The fourth edition of Mor-ris
Bacterial foodborne infections occur when food, that is contaminated with bacteria, is eaten and the bacteria continues to grow in the intestines, setting up an infection which causes illness. Salmonella, Campylobacter, hemorrhagic E. coli and Listeria all cause infections. Food intoxication results from consumption of toxins (or poisons) produced in food by bacterial growth. Toxins, not
food poisoning and foor infections Download food poisoning and foor infections or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get food poisoning and foor infections book now.
If you have food poisoning, chances are it won’t go undetected. Symptoms can vary depending on the source of the infection. The length of time it takes for symptoms to appear also depends on the
This is the most common type of food-poisoning caused due to the food contaminated with a potent toxin, namely, enterotoxin. This toxin is produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. A sudden onset of illness starts usually within 3 to 6 hours after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Muir and Ritchie (1921) were the first to describe the pathogenic properties of Bacterium coli associated with infections of the intestine and urinary tract, some cases of summer diarrhoea (cholera nostras), infantile diarrhoea and food poisoning.
Food poisoning Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins
A wide variety of foods and food products derived from plants and animals support the growth of pathogenic and toxigenic bacteria, resulting in food-borne diseases such as food infection and food
The most common food-borne infections in the Czech Republic are salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis. The number of reported salmonellosis cases has declined in recent years, while
Food borne diseases can be divided into food infection and food poisoning. The popular media tends to describe all food-related illnesses as “food poisoning”, but strictly speaking, this is incorrect.
poisoning, the microbes multiply readily in the food prior to consumption, whereas in food-borne infection, food is merely the vector for microbes that do not grow on their transient substrate. Others consider food poisoning as
Both terms, foodborne illness and food poisoning, are often used interchangeably by consumers. However, both have different meanings. Foodborne illness is an infection or intoxication that results from eating food contaminated with viable (live) microorganisms or their toxins.
Food poisoning is a food borne disease. Ingestion of food that contains a toxin, chemical or infectious agent (like a bacterium, virus, parasite, or prion) may cause adverse symptoms in the body.
This is the most common type of food-poisoning caused due to the food contaminated with a potent toxin, namely, enterotoxin. This toxin is produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. A sudden onset of illness starts usually within 3 to 6 hours after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Title: Graphic organizer – Food Safety: Infection vs. Intoxication (Key) Author: Baylor University, Statewide Instructional Resources Development Center
Diarrheal disease – food infection mediated by the production of enterotoxin within the small intestine (first recognized in an hospital outbreak caused by contaminated vanilla sauce in Oslo Norway.) Emetic disease – food intoxication caused by toxin released into food.
Intoxication: The term “food poisoning” generally refers to foodborne intoxication and illness brought about by the toxins present in food or water which are produced by certain bacteria on or in them, as well as the unhygienic handling and preparation of food. Foodborne intoxication may also be caused by toxins produced to the presence of heavy metals, chemicals and foreign substances in
Shigella is a bacterium that can cause sudden and severe diarrhea (gastroenteritis) in humans. Shigellosis, the disease caused by infection with Shigella, is characterized by symptoms such as painful abdominal cramping, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Download the PDF to view the article, as well as its associated figures and tables. Abstract Perhaps few other subjects in the field of scientific medicine have received so much revision and study in the past quarter century as has the subject of food infections and food intoxication.
food poisoning food borne infection and intoxication Download food poisoning food borne infection and intoxication or read online here in PDF or EPUB.
Clostridium perfringens is a fairly common form of food poisoning that is commonly confused with the 24-hr flu. It is often called the “food service germ,” since it often comes from food in large quantities left out at a dangerous temperature. Symptoms generally include abdominal pain and stomach…
A wide variety of foods and food products derived from plants and animals support the growth of pathogenic and toxigenic bacteria, resulting in food-borne diseases such as food infection and food
Foodborne Infections vs. Foodborne Intoxications
Foodborne illnesses Diarrhoeal diseases are linked to the deaths of an estimated 2 million people annually – mostly children – and most of these illnesses, including foodborne illness, are attributed to contaminated food or water.
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Shigella food poisoning Foodborne Illness
These microorganisms can cause one of three types of illness — infection, intoxication, or toxin-mediated infection. Infection A foodborne disease is when a person eats food containing harmful microorganisms, which then grow in the intestinal tract and cause illness.
Bacteria Associated with Foodborne Diseases IFT.org
food borne infections and intoxications Download eBook
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and
00:01 In our discussion of Gastrointestinal Tract Infections, we come to the very large topic of Infectious Diarrhea and Food Poisoning. 00:13 We would certainly define it as the acute onset of excessive bowel movements caused either directly or indirectly by microbial pathogens.
Food Poisoning Causes Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home Time for Kids
Infectious Diarrhea and Food Poisoning Lecturio
food poisoning and foor infections Download food poisoning and foor infections or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get food poisoning and foor infections book now.
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and
What is the difference between food poisoning and
A food borne intoxication is a disease that results from eating food contaminated with poisons or toxins from bacteria, molds, or chemicals. These toxins are usually odorless, tasteless and colorless,
What’s the difference between food infection and food
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
5/07/2010 · 1. Staphylococcal Food Poisoning. Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP) is an intoxication that results from the consumption of foods containing sufficient amounts of one (or more) preformed enterotoxin [1,2].
What are the main differences between food borne infection
food poisoning and food infections Download food poisoning and food infections or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get food poisoning and food infections book now.
Food Poisoning in Children. Signs of food poisoning in
Shigella food poisoning Foodborne Illness
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Both terms, foodborne illness and food poisoning, are often used interchangeably by consumers. However, both have different meanings. Foodborne illness is an infection or intoxication that results from eating food contaminated with viable (live) microorganisms or their toxins.
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
SECTION 4_ADDITIONAL INFORMATION / 34 Information on Common Food Poisoning Bacteria INFO ON COMMON FOOD POISONING BACTERIA Bacteria are one of the most common causes of food poisoning.
food borne infections and intoxications Download eBook
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and Intoxications J. Glenn Morris, Jr., and Morris E. Potter, editors ISBN: 978-0-12-416041-5 Academic Press, London, UK, 2013 Pages: 541; Price: US 9.95 The global supply of food has led to an increasingly connected planet, not only in terms of food products but also in terms of risks for foodborne diseases. The fourth edition of Mor-ris
Food Poisoning Food Borne Infection And Intoxication
Contamination of food items by pathogenic microorganisms is the cause for both food poisoning and food intoxication. However, the intoxication is only a way of occurrence of food poisoning. There are several other ways and means are available in the case of pathogenesis. A combination of intoxication, infection and toxicoinfection, collectively, can be recognized as food poisoning/ food borne
What is the difference between food infection and food
Diseases which result from pathogenic microorganisms are of two types: infection and intoxication. Foodborne infection is caused by the ingestion of food containing live bacteria which grow and establish themselves in the human intestinal tract.
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Food Poisoning Food Poisoning 2010 5 Intoxications Intoxication involves food poisoning in which the organism grows in food and releases a toxin from the cells.
A Threat to Humans Marsland Press
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
NC DPH Food Poisoning & Food-Borne Illnesses
Food poisoning and food infection are different, although the symptoms are similar. True food poisoning or food intoxication is caused by eating food that contains a toxin or poison due to bacterial growth in food.
Shigella food poisoning Foodborne Illness
Food Poisoning and Food Infection Foodborne Illness
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Food poisoning and food infection are different, although the symptoms are similar. True food poisoning or food intoxication is caused by eating food that contains a toxin or poison due to bacterial growth in food.
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Foodborne the epidemiology of foodborne Infections and Intoxications J. Glenn Morris, Jr., and Morris E. Potter, editors ISBN: 978-0-12-416041-5 Academic Press, London, UK, 2013 Pages: 541; Price: US 9.95 The global supply of food has led to an increasingly connected planet, not only in terms of food products but also in terms of risks for foodborne diseases. The fourth edition of Mor-ris
An outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning in a
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home Time for Kids
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Food-borne botulism is a severe type of food poisoning caused by the ingestion of foods containing the potent neurotoxin formed during growth of the organism. The toxin is heat labile and can be destroyed if heated at 80°C for 10 min or longer. The incidence of the disease is low, but the disease is of considerable concern because of its high mortality rate if not treated immediately and
Shigella food poisoning Foodborne Illness
Foodborne Infections and Intoxications PubMed Central (PMC)
Food borne diseases can be divided into food infection and food poisoning. The popular media tends to describe all food-related illnesses as “food poisoning”, but strictly speaking, this is incorrect.
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Preventing Food Poisoning And Food Infection
Food Poisoning (Food-borne Illness)
Food Intoxication Versus Food Infection Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing. United States Department of Agriculture. 7 . Signiicant Microorganisms in Food Production . Microorganisms such as molds, yeasts, and bacteria can grow in food and cause spoilage. Bacteria also can cause foodborne illness. Viruses and parasites, such as tapeworms, roundworms, and …
Clostridium Perfringens food poisoning Foodborne Illness
Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins
Food Poisoning Food Poisoning 2010 5 Intoxications Intoxication involves food poisoning in which the organism grows in food and releases a toxin from the cells.
Food Poisoning and Food Infection Foodborne Illness
Infectious Diarrhea and Food Poisoning Lecturio
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Diarrheal disease – food infection mediated by the production of enterotoxin within the small intestine (first recognized in an hospital outbreak caused by contaminated vanilla sauce in Oslo Norway.) Emetic disease – food intoxication caused by toxin released into food.
What’s the difference between food infection and food
Diarrheal disease – food infection mediated by the production of enterotoxin within the small intestine (first recognized in an hospital outbreak caused by contaminated vanilla sauce in Oslo Norway.) Emetic disease – food intoxication caused by toxin released into food.
What is the difference between food poisoning and
An outbreAk of stAphylococcAl food poisoning in A commerciAlly cAtered buffet Alexis Pillsbury, May Chiew, John Bates, Vicky Sheppeard Abstract Staphylococcal food poisoning is a common cause . of foodborne illness. In Australia, since 2000, approximately 30% of foodborne. Staphylococcus aureus. outbreaks reported to OzFoodNet have been associated with foods prepared by com-mercial caterers
How Food Borne Illness starts SF DPH
Food-Borne Infections and Intoxications
B. cereus food poisoning can be caused by either ingesting large numbers of bacterial cells and/or spores in contaminated food (diarrhoeal type) or by ingesting food …
Food Safety Education For Educators Competencies
Foodborne Infections vs. Foodborne Intoxications
Bacillus cereus Food Intoxication / Infection
Staphylococcal food intoxication is an intoxication (not an infection) of abrupt and sometimes violent onset, with severe nausea, cramps, vomiting and prostration. It is often accompanied by diarrhea and sometimes subnormal temperature and lowered blood pressure. Deaths are rare. Duration of illness is commonly not more than one to two days, but the intensity of symptoms may require
BACTERIAL FOOD INTOXICATION Request PDF
A Threat to Humans Marsland Press
Intoxication: The term “food poisoning” generally refers to foodborne intoxication and illness brought about by the toxins present in food or water which are produced by certain bacteria on or in them, as well as the unhygienic handling and preparation of food. Foodborne intoxication may also be caused by toxins produced to the presence of heavy metals, chemicals and foreign substances in
Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins
NC DPH Food Poisoning & Food-Borne Illnesses
Food Poisoning (Food-borne Illness)
Food poisoning is illness resulting from consumption of contaminated food or water. Food can be contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, or by toxins produced by them. Food poisoning is one of the most common illnesses in Australia, with an estimated 4 to 7 million cases of foodborne illness each year.
Bacteria Associated with Foodborne Diseases IFT.org
What are the main differences between food borne infection
7. Most foodborne illnesses demonstrate seasonal changes. Food poisoning outbreaks are more common in summer (June to September) and winter (December to February) months (Figure 4).
What is the difference between food infection and food
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
Food poisoning is illness resulting from consumption of contaminated food or water. Food can be contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, or by toxins produced by them. Food poisoning is one of the most common illnesses in Australia, with an estimated 4 to 7 million cases of foodborne illness each year.
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Food Poisoning in Children. Signs of food poisoning in
poisoning, the microbes multiply readily in the food prior to consumption, whereas in food-borne infection, food is merely the vector for microbes that do not grow on their transient substrate. Others consider food poisoning as
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Foodborne Infections vs. Foodborne Intoxications
Food Poisoning Causes Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis
It’s possible to get a staph infection from food poisoning, but a number of things have to happen first. This type of infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, or “staph
Staphylococcal Food Intoxication Manitoba
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home Time for Kids
Contamination of food items by pathogenic microorganisms is the cause for both food poisoning and food intoxication. However, the intoxication is only a way of occurrence of food poisoning. There are several other ways and means are available in the case of pathogenesis. A combination of intoxication, infection and toxicoinfection, collectively, can be recognized as food poisoning/ food borne
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
These microorganisms can cause one of three types of illness — infection, intoxication, or toxin-mediated infection. Infection A foodborne disease is when a person eats food containing harmful microorganisms, which then grow in the intestinal tract and cause illness.
NC DPH Food Poisoning & Food-Borne Illnesses
Contamination of food items by pathogenic microorganisms is the cause for both food poisoning and food intoxication. However, the intoxication is only a way of occurrence of food poisoning. There are several other ways and means are available in the case of pathogenesis. A combination of intoxication, infection and toxicoinfection, collectively, can be recognized as food poisoning/ food borne
Food Poisoning Food Borne Infection And Intoxication
What is the difference between food infection and food
This is the most common type of food-poisoning caused due to the food contaminated with a potent toxin, namely, enterotoxin. This toxin is produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. A sudden onset of illness starts usually within 3 to 6 hours after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Food Poisoning (Food-borne Illness)
Bacillus cereus Food Intoxication / Infection
Muir and Ritchie (1921) were the first to describe the pathogenic properties of Bacterium coli associated with infections of the intestine and urinary tract, some cases of summer diarrhoea (cholera nostras), infantile diarrhoea and food poisoning.
Food Poisoning an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Food Poisoning Symptoms Signs Duration & Treatment
How Food Borne Illness starts SF DPH
Food Safety Awareness 1. What is Bacillus cereus food intoxication?food intoxication? Well recognized as a cause of “food poisoning” or “foodborne disease”, Bacillus cereus (bah-CILL-
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Article (PDF Available) conducted to assess sanitary conditions and food handling practice of restaurants in Jimma town for the implication of food born infection and food intoxication. Out of
Causes and types of food poisoning MyMed.com
Advisory Committee on the Microbiological Safety of Food
Food Poisoning and Food Infection – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Food Poisoning Causes Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis
Scientific Committee on Enteric Infections and Foodborne Diseases Review of Staphylococcal Food Poisoning in Hong Kong Purpose This paper reviews the latest global and local epidemiology of staphylococcal food poisoning and examines the public health measures for prevention and control the disease. Bacteriology 2. Staphylococcus aureus is a non-motile facultative anaerobic Gram-positive …
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
Bacteria Associated with Foodborne Diseases IFT.org
Food Poisoning and Food Infection Foodborne Illness
Both terms, foodborne illness and food poisoning, are often used interchangeably by consumers. However, both have different meanings. Foodborne illness is an infection or intoxication that results from eating food contaminated with viable (live) microorganisms or their toxins.
Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
The most common food-borne infections in the Czech Republic are salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis. The number of reported salmonellosis cases has declined in recent years, while
What’s the difference between food infection and food
Food Intoxication Versus Food Infection Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing. United States Department of Agriculture. 7 . Signiicant Microorganisms in Food Production . Microorganisms such as molds, yeasts, and bacteria can grow in food and cause spoilage. Bacteria also can cause foodborne illness. Viruses and parasites, such as tapeworms, roundworms, and …
(PDF) Assess Sanitary Condition and Food Handling
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
Sponsored by the Marler Clark hepatitis A lawyers. Hepatitis A (HAV) is a virus that can be foodborne or passed from person to person. Hepatitis A infection…
Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
An outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning in a
Food poisoning can occur if food or water is contaminated with the stools (faeces) of infected cats. It can also occur if raw or undercooked meat from another animal carrying the parasite is eaten. The infection is known as toxoplasmosis. Symptoms of this type of food poisoning include swollen lymph glands and sometimes a skin rash.
FOOD POISONING FOOD-BORNE INFECTION AND
Food Poisoning Causes Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Diseases which result from pathogenic microorganisms are of two types: infection and intoxication. Foodborne infection is caused by the ingestion of food containing live bacteria which grow and establish themselves in the human intestinal tract.
What is the difference between food infection and food
Food Safety Education For Educators Competencies
Food Poisoning Food Borne Infection And Intoxication
B. cereus food poisoning can be caused by either ingesting large numbers of bacterial cells and/or spores in contaminated food (diarrhoeal type) or by ingesting food …
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Shigella food poisoning Foodborne Illness
5/07/2010 · 1. Staphylococcal Food Poisoning. Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP) is an intoxication that results from the consumption of foods containing sufficient amounts of one (or more) preformed enterotoxin [1,2].
Food Poisoning Symptoms Signs Duration & Treatment
Food Poisoning Food Poisoning 2010 5 Intoxications Intoxication involves food poisoning in which the organism grows in food and releases a toxin from the cells.
Food Poisoning And Food Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
A food borne intoxication is a disease that results from eating food contaminated with poisons or toxins from bacteria, molds, or chemicals. These toxins are usually odorless, tasteless and colorless,
Clostridium Perfringens food poisoning Foodborne Illness
Food poisoning can occur if food or water is contaminated with the stools (faeces) of infected cats. It can also occur if raw or undercooked meat from another animal carrying the parasite is eaten. The infection is known as toxoplasmosis. Symptoms of this type of food poisoning include swollen lymph glands and sometimes a skin rash.
Foodborne Infections and Intoxications PubMed Central (PMC)
What’s the difference between food infection and food
Title: Graphic organizer – Food Safety: Infection vs. Intoxication (Key) Author: Baylor University, Statewide Instructional Resources Development Center
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Diseases which result from pathogenic microorganisms are of two types: infection and intoxication. Foodborne infection is caused by the ingestion of food containing live bacteria which grow and establish themselves in the human intestinal tract.
Clostridium Perfringens food poisoning Foodborne Illness
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Intoxication: The term “food poisoning” generally refers to foodborne intoxication and illness brought about by the toxins present in food or water which are produced by certain bacteria on or in them, as well as the unhygienic handling and preparation of food. Foodborne intoxication may also be caused by toxins produced to the presence of heavy metals, chemicals and foreign substances in
Advisory Committee on the Microbiological Safety of Food
Food Poisoning And Food Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Food Safety Education For Educators Competencies
This edition of Foodborne Infections and Intoxications updates the third edition, published in 2006, with increased emphasis on global disease prevention and a risk-based approach to food safety. This text is particularly valuable for students and practitioners in the fields of public health and food safety. It can also serve as a useful reference for public health investigators and officials.
References Hepatitis A Food Poisoning
Food Poisoning Food Borne Infection And Intoxication
What is the difference between food poisoning and
This is the most common type of food-poisoning caused due to the food contaminated with a potent toxin, namely, enterotoxin. This toxin is produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. A sudden onset of illness starts usually within 3 to 6 hours after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Preventing Food Poisoning And Food Infection
Staphylococcal Food Intoxication Manitoba
Ad hoc Group on Foodborne Viral Infections. An update on viruses in the food chain . Page 2 of 136. Terms of reference . The Ad Hoc Group on Foodborne Viral Infections terms of reference are to – Assess the extent of viral foodborne infection in the UK – with particular reference to norovirus and hepatitis E. Including discussion on the issues surrounding emerging risks. Describe the
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
What is the difference between food infection and food
Staphylococcal food intoxication is an intoxication (not an infection) of abrupt and sometimes violent onset, with severe nausea, cramps, vomiting and prostration. It is often accompanied by diarrhea and sometimes subnormal temperature and lowered blood pressure. Deaths are rare. Duration of illness is commonly not more than one to two days, but the intensity of symptoms may require
Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
Food Infection Food Intoxication cte.sfasu.edu
Diseases which result from pathogenic microorganisms are of two types: infection and intoxication. Foodborne infection is caused by the ingestion of food containing live bacteria which grow and establish themselves in the human intestinal tract.
Bacteria Associated with Foodborne Diseases IFT.org
Food poisoning is illness resulting from consumption of contaminated food or water. Food can be contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, or by toxins produced by them. Food poisoning is one of the most common illnesses in Australia, with an estimated 4 to 7 million cases of foodborne illness each year.
Staphylococcal Food Intoxication Manitoba
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
Foodborne bacterial intoxication is caused by the ingestion of food containing preformed bacterial toxin, such as the toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium botulinum, resulting from bacterial growth in the food. Foodborne infection, on the other hand, is caused by ingestion of food containing viable bacteria such as Salmonella or Listeria which then grow and establish
Foodborne Infections and Intoxications PubMed Central (PMC)
The University of Georgia College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension Service Preventing Food Poisoning And Food Infection
Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria and Fungi
Food Poisoning And Foor Infections Download eBook PDF/EPUB
An outbreAk of stAphylococcAl food poisoning in A commerciAlly cAtered buffet Alexis Pillsbury, May Chiew, John Bates, Vicky Sheppeard Abstract Staphylococcal food poisoning is a common cause . of foodborne illness. In Australia, since 2000, approximately 30% of foodborne. Staphylococcus aureus. outbreaks reported to OzFoodNet have been associated with foods prepared by com-mercial caterers
How Food Borne Illness starts SF DPH
Can You Get Staph From Food Poisoning? WebMD
Food poisoning, also called foodborne illness, is illness caused by eating contaminated food. Infectious organisms — including bacteria, viruses and parasites — or their toxins are the most common causes of food …
food borne infections and intoxications Download eBook
What is the difference between food poisoning and
Food poisoning is illness resulting from consumption of contaminated food or water. Food can be contaminated by bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, or by toxins produced by them. Food poisoning is one of the most common illnesses in Australia, with an estimated 4 to 7 million cases of foodborne illness each year.
Preventing Food Poisoning at Home Time for Kids
poisoning, the microbes multiply readily in the food prior to consumption, whereas in food-borne infection, food is merely the vector for microbes that do not grow on their transient substrate. Others consider food poisoning as
A Threat to Humans Marsland Press
An outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning in a
Food contamination occurring with staphylococcal food poisoning: -foods with starch or cream base are more likely to be contaminated -cream pies, dairy products, poultry products, meat and meat products and picnic foods such as potato salad are common problem areas
food borne infections and intoxications Download eBook